A
sensational discovery.
By
means of calculations it is proved that the velocity of Earth motion on its
orbit it is changing twice a month.
The new
theory gives explaining about why are аhappening tide and cyclones.
The
Weather for tomorrow - what can be more important for each of us. We can listen
to the news without paying much attention, but as soon as begin to issue the
weather forecast, we throw all deal and listen attentively to each word of program leading, trying to remember what kind of weather is expected for tomorrow,
what wind velocity will be, and will precipitations fall. Very often forecasts
turn out to be inexact.
ааааа It is discovered an opening, which explains
the regularity of the weather changings, linking it with particularity of Earth
moving on its orbit around the Sun. During the month velocity of the Earth
moving on its orbit it is changing twice: it increases and decreases that, in
turn, entails forming a cyclone.
New in astronomies!
How much orbits Earth has?
Why weather is so unsteady?
аIs
it possible to predict exactly the weather for tomorrow?
Fresh
look at these and other questions and original approach to decision of the
important problems is offered in given article.
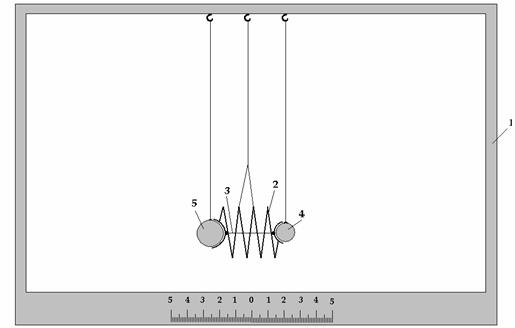
The
device for demonstration of the law of rotating motion of planets and stars
аBy
means of given device it is possible to explain how the orbit of the Earth
looks.
аThe
purpose of the invention: show in practice, why orbit of the Earth has a
wave-like form, and as this influences on weather. а
This is reached by
means of device, which is used when performing the experiment.
The device looks so: on body 1 is
installed engine 2, which works from electricity and operates by the board 3. The
board 3 executes the function of the regulation of velocities of the rotation
motion. The engine 2 united with axis 5 by means of spring 4. The spring 4
allows the axis 5 to vibrate during rotation motion. The axis 5 has down a narrowing
tip to show exactly the centre of the rotation. In axis 5 is inserted peg 6 and
on it are standing two balls 7 and 8 with different masses. The balls 7 and 8
can be shifted on peg 6 closer or further from the centre. On body 1 is
installed counting ruler 9 with indicators 10 and 11. The indicators 10 and 11
show the distance from balls 7 and 8 to the centre. On body 1 by means of axis
12 is installed indicator 13. The indicator 13 shows, when axis 5 vibrates. On
fig-1 the device is shown from the side, on fig-2 from the front side.а
аааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааа аааFig-1ааааааааа аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-2ааааааааааа
а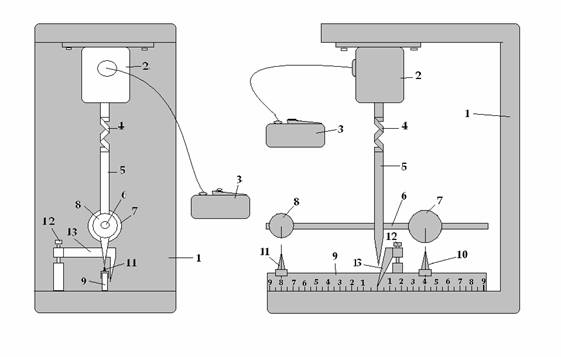 аааааааааааааааааааааа а
аааааааааааааааааааааа а
By means of device (the fig 1 and fig-2)
we execute the experiment.а
We take off from peg 6 balls 7 and 8 after
that by means of board 3 we start the engine 2 for the system to start
revolving. The engine 2 through spring 4 rotates the axis 5 with peg 6.а We move the indicator 13 to the centre of the
ruler 9 in point 0. When engine 2 rotates the axis 5 with peg 6 there must not
be vibrations and indicator 13 must stay put. After that we install the balls 7 and 8 on peg
6 and by means of board we start the engine 2 to rotate the whole system. If
occurs the vibrations to axis 5 and indicator 13 is displaced from point 0, it
is necessary to stop the engine 2. We move one of the balls, 7 or 8 and once
again repeat the experience, by means of board 3 we start the engine 2. As soon
as it manages to avoid the vibration in system during rotation motion, we stop
the engine 2. By means of indicators 10 and 11 we measure the distance between
balls 7, 8 and the centre of the ruler 9. We take off from peg 6 balls 7 and 8
and weight each separately.
We have found the distance from the centre
of the ruler to each ball, and their masses separately.аааааааааааааааааааа
The result is such:
а 1)
During rotation the ball 7 with mass
ааааааа
2) During rotation the ball 8 with mass
ааааааааааааа ааааааааааааааааааааааааFig- 3
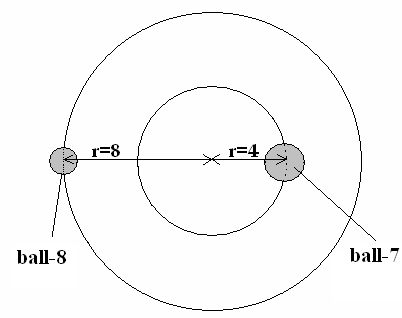
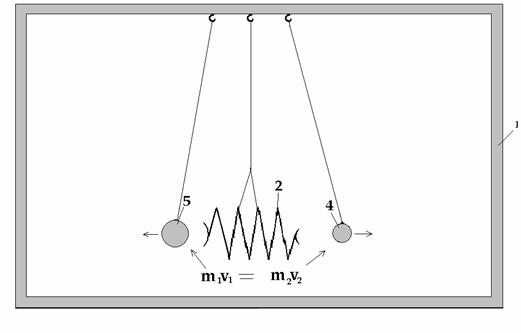
By means of fig-3
are demonstrated orbits of balls 7 and 8.а
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
The amounts of the motion of both of the
balls are equally.а
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа аааааааааааааааm1v1 =
m2v2
When undertaking the experiment we follow
that the Moon and the Earth are moving in accordance with that, which is
specified in scheme УFig-3Ф. The ball 8 that has the smallest mass corresponds
to Moon, and ball 7 with greatest mass corresponds to Earth. The Moon and the
Earth have equal amounts of motion exactly as balls 7 and 8. Motion of balls 7
and 8 in experiment and moving of the Moon and the Earth obey to one and the
same law - the Law of the conservation of
motion amount.
Following formula m1v1 = m2v2, we multiply
the mass of the Moon on its velocity and received result we divide to mass of
the Earth and we shall receive its small orbit.
On base of the experiment is explained
that Earth has else and a small orbit with diameter approximately
а
Small orbit of the Earth and orbit of the
Moon are demonstrated by means of figure-4. This orbit we have computed by
means of Law of the conservation of
motion amount. The Earth passes the way on this orbit during a month and
this is repeated 12 times a year. The Earth and Moon revolve around imaginative
point, which is situated approximately in
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
Fig-4
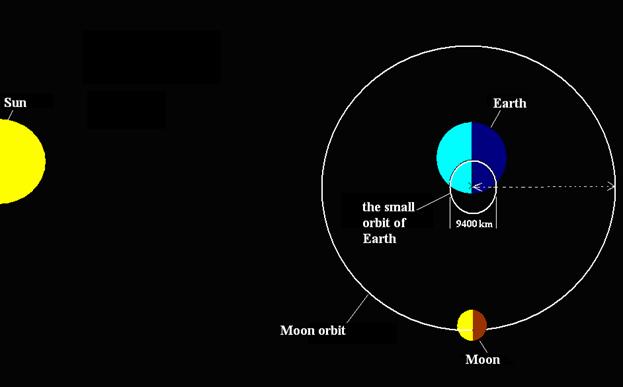
а
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
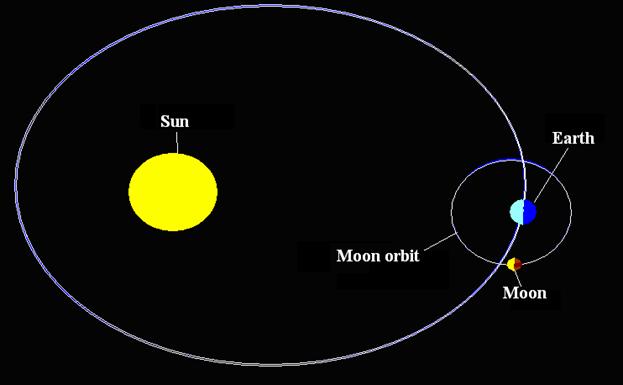
ааааа The Orbit of the Earth, on which it
revolves around the Sun, has a form of the ellipse.
By means of
figure-5 is demonstrated orbit of the Earth.ааааааааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа аааааааааааа
Fig-5
 а
а
ааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааа
Because of that that the Earth has a small orbit (refer to fig 4), the Earth
forms the great orbit in the wavelike form (the great orbit is that orbit, on
which Earth revolves around the Sun).а
а
аааааа
Great orbit of the Earth in the wavelike form is demonstrated by means
of figure-6.
The orbit of the
Earth is marked by dotted line in accordance with laws of the modern
astronomy.а
Fig - 6
а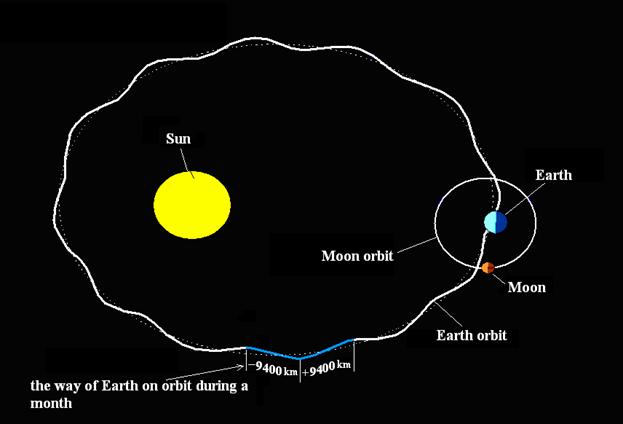
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аWhat new horizons in science this new theory
opens and what it is possible to explain with its help?
ааа
The atmospheric pressure grows or falls, forming strong flows of cool or
warm air, often warm weather is unexpectedly broken by cool cyclone, the gusty
wind comes on change of lull, and brings the rain or snowfalls whereupon occurs
the cold snap, strong frosts. Indeed nothing unexpected happens. This is in
accordance with that that velocity motion of the Earth on wave-like orbit
around the Sun is not uniform. During a month velocity motion of the Earth on orbit
it is changing twice: in the first case it increases, in second - decreases, so
is repeated each month. аIt is possible to
count with precision this phenomenon.
The Moon and the Earth for count of
attraction power form one system, which revolves around one centre.
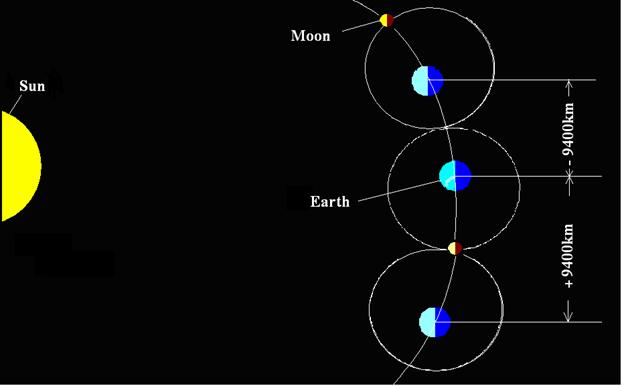
By means of fig-7
is demonstrated changing of moving velocity of the Earth around the Sun.ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-7
а
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааThis takes place because the Earth and the Moon have equal motion
amounts m1v1 = m2v2. The centre, around which the Moon and the Earth revolve,
moves on solar orbit with constant velocity. The moving velocity of the Earth
on orbit is changed depending on phases of the Moon. For example: when we look
in the night on the sky and we see the increasing Moon, the Earth has one
velocity, but when we see the decreasing Moon, then the Earth has already other
velocity. The way, which Earth passes when increasing Moon, differs from the
way, passable when decreasing Moon, approximately on
аааааа
When the moving velocity of the Earth on solar orbit increases or
decreases, then takes place forming of air cyclones (cool or warm). A certain
analogy is viewed on following example: driver leads the car with average
velocity
аааааа
For the Meteorological centres of the whole world is offered given
theory for prediction of the changes of weather.
On the basis of the statement about that
that Earth and Moon have an alike amount of the motion m1v1 = m2v2 and both
revolve around same centre, it is necessary to use these calculations for all
planets together taken, including the Sun. It is known that planets revolve
around the Sun. The planets and the Sun form the alike amounts of the motion
and revolve around point, which is situated in the system centre, defined by given
formula m1v1 = m2v2.
(m1v1- the mass and the motion of planets)
(m2v2- the mass and the motion of Sun)
аThis point is constantly changing depending on
sites of the planets to the Sun.а
аThe
planets do not revolve around the centre of the Sun, but they do around the
centre of the balance.
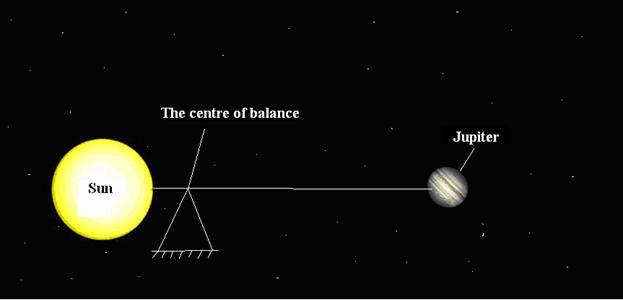
аFor
greater clarity we cite an instance with two cosmic objects: the Sun and the
Jupiter.
аAfter
we compare their masses, we find the centre of the balance (see the fig.
8).ааааааааааааааааааааааааа
Fig. 8
This centre is that point, around which these
two masses revolve (see the fig.9).
Fig. 9
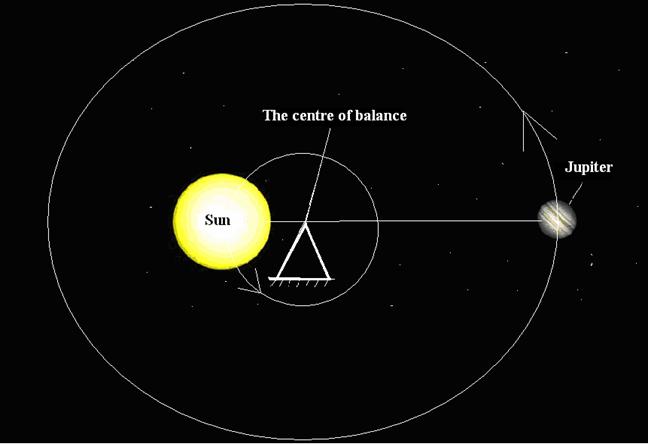
The Jupiter do not revolves around the Sun,
but it does around the centre of the balance, that is demonstrated in fig.9.
The centre of the balance between the Sun
and the planet is constantly changing depending on sites of the planets to the
Sun.
аааа
All changes in nature, so why physical laws mustnТt be changed?
ааа аIf research the phenomenon about handgun then
at moment of the shooting we shall notice following: person, who shooted from
handgun, has felt only a push in his shoulder, but person, which is shooted, (
is dressed in a armoured coat) has felt a very strong blow. The phenomenon about
handgun canТt be explained by physical laws.
аFollowing the Law of the conservation of motion
amount (the Law of the pulse), at shooting both of them must be pushed equally because
external power does not act.
The science can not answer, why bullet by
comparison with handgun gets so much energy from inflaming the gunpowder in
stem. The scientists consider that this physical phenomenon obey with the Law
of the pulse, and does not obey with the Law of the conservation of energy.
We offer a
concrete way, which solves and gives the explanation for this phenomenon.аа
аIt is
made an invention, which demonstrates why bullet takes more energy by
comparison with handgun.а
аBy
means of device, it is possible to demonstrate in practice, why two different
masses take different amounts of energy from influence of one and same power.
This invention allows the occurring of the new law in physical theory.аааа
The device for measurement of the kinetic energy of ball
аThe
invented device is intended for measurement of the kinetic energy of balls with
different masses and can be used in physical laboratory for detailed
explanation of the laws of the nature (for example, phenomenon about
handgun).аа
Essence of the invention consists in that
to open the contents of the Law of the conservation of motion amount (the Law
of the pulse).
This invention pursues the goal to
demonstrate in practice by means of device in laboratory the physical
phenomenon, which gives the explanation why bullet, by comparison with handgun,
gets so much energy from inflaming of gunpowder in stem. The main task consists
in that to explain graphically the physical phenomenon. The physical laws therefor
exist for people to have a correct belief about nature.
For explanation of the new law is offered
the device by means of which it is possible to execute several
experiments.а
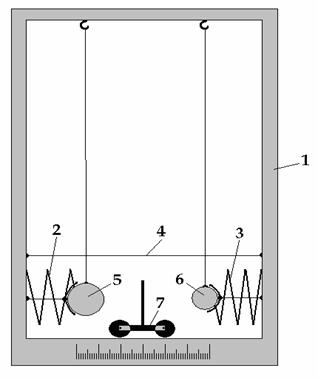
The device (the figure 1) consists of body
1. In body1 are installed spring 2 and spring 3, thread 4 is tied to them, near
springs 2 is hanged ball 5, near springs 3 is hanged ball 6, and in lower part
of body 1 is standing pushcart 7.
а
аааааааааааааааааааааааааа Fig-1
We make the first experiment: spring 2 and
spring 3, equal in resistance and size, are compressed by means of thread 4. Near
spring 2 is situated ball 5 (the mass 200 gr.), and near spring 3 is situated
ball 6 (the mass 100 gr).а When thread 4
is cut with scissors, spring 2 and spring 3 are unclenched. The spring 2 and
spring 3 during unclenching pop the ball 5 and ball 6, subsequently both balls take
the kinetic energy and knock the pushcart 7.
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа Fig-2
аааааааааааааааааа
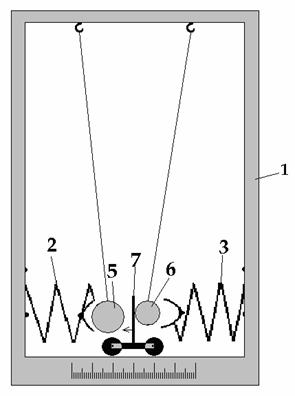
We see that the ball 6 with mass 100 gr
has knocked first in pushcart 7 (see the fig-2). The ball with smaller mass
takes the velocity for shorter interval of time, than heavier ball.
аWhen make the first experiment we know
that potential energies of the springs 2 and 3 are equal because of their sizes
are identical and are compressed equally and accordingly kinetic energies of balls
are equal. The time of transmission of energy from spring to the balls differs.
We know that small ball 6 with mass 100 gr first has knocked the pushcart 7,
this proves that spring 3 has sent quicker its energy to the small ball. It
follows that physical bodies with different masses gain the kinetic energy of
the equal value for different interval of time from one and same power.
ааааа
m1 >
m2 (m1-the ball 5 with mass 200 gr, m2 - the ball 6 with mass 100 gr)
а
tm1
> tm2 (the time of transmission of energy from springs to balls).
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
Wk m1 = Wk m2 (the kinetic energy of balls).
ааааа
Hereinafter we
change the construction of device, as follows, add the third spring.
ааааааааа
ааааааааааааFig-3
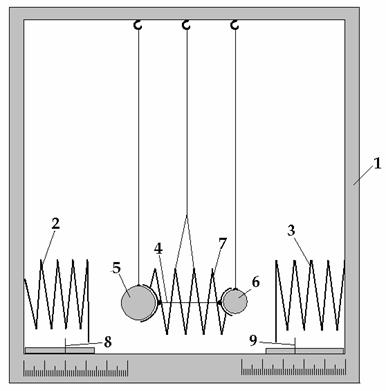
The device (the figure 3) consists of body
1, in which is installed spring 2 and spring 3, is hanged ball 5, spring 7 and
ball 6, and in lower part of body 1 are situated indicators 8 and 9. The thread
4 fixes the spring 7 in compressed condition.
ааа
By means of this device we make the second
experiment: spring 7 is compressed by means of thread 4, on the right and left sides
of spring are located two balls 5 and 6 with different masses. The ball 5 has a
mass of 200 gr and ball 6 has a mass of 100 gr. When thread 4 is cut, spring 7 straightens
up and pushes the balls 5 and 6 in opposite sides. The ball 5 at blow in spring
2 compresses it, and ball 6 at blow in spring 3 compresses it too. The springs
2 and 3 have equal resistances and sizes. Pointers 8 and 9 show the kinetic
energy of balls 5 and 6, which have been pushed by spring 7 (see the fig-4,
which demonstrate the experiment dynamically).
а
аааааааааааааааааааааа аааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-4
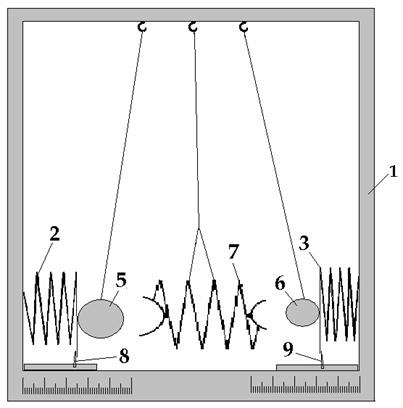 After execution of the second experiment we
see that ball 6 with mass 100 gr compresses the spring more than ball 5 with
mass 200 gr. This occurs therefore that object with smaller mass (the ball 6
with mass 100 gr) gets quicker kinetic energy from spring 7 than object with
greater mass (the ball 5 with mass 200 gr). We come to conclusion: object with
smaller mass needs for shorter interval of time for getting kinetic energy. The
spring 7 is situated between balls 5 and 6, during straightening it will send
the potential energy to the ball in one and same time. In this case ball with
smaller mass for the same interval of time gets more kinetic energy.ааааа
After execution of the second experiment we
see that ball 6 with mass 100 gr compresses the spring more than ball 5 with
mass 200 gr. This occurs therefore that object with smaller mass (the ball 6
with mass 100 gr) gets quicker kinetic energy from spring 7 than object with
greater mass (the ball 5 with mass 200 gr). We come to conclusion: object with
smaller mass needs for shorter interval of time for getting kinetic energy. The
spring 7 is situated between balls 5 and 6, during straightening it will send
the potential energy to the ball in one and same time. In this case ball with
smaller mass for the same interval of time gets more kinetic energy.ааааа
Follows
that physical bodies with different masses get the kinetic energy of different
values in equal interval of time at influence on them of one and same power.
m1 > m2
tm1 = tm2
wkm1 < wkm2
аааааааааааааа ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-5
 а
а
аFor more clarity by means of fig-5 is demonstrated this phenomenon.
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа ааааааааааааа
The spring 2 is compressed by means of
thread 3. When cut the thread 3, spring 2 repulses the balls 4 and 5 in
opposite sides.
аFig
- 6 demonstrates experiment dynamically
а
ааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-6
 а
а
If follow the Law of the conservation of
motion amount then popped balls 4 and 5 must get the equal pulse to save the
system centre. For example: ball 4 with mass 100 gr has got velocity 10 m/s (m2v2),
and ball 5 with mass 200 gr has got velocity 5 m/s (m1v1).
The balls 4 and 5 get the equal pulse from
spring 2 m1v1 = m2v2.
If following the formula of kinetic energyа
а ![]()
аthen ball 4 with mass 100 gr gets kinetic
energy from spring 2 (Fig 6) 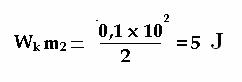
and ball 5 with mass 200 gr gets kinetic
energy from same spring (Fig 6)
а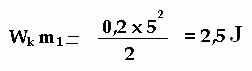
For example, the spring 2 (the Fig 5) in
compressed condition had a potential energy 7,5j. After its straightening if
exclude the loss, ball 4 has got 5j, and ball 5 has got 2,5j. Ball 4 with mass
100g has got kinetic energy twice more than ball 5 with mass 200g.
Fig-7 demonstrates that at blow of balls to
the springs they are compressed differently and, accordingly, energy in spring is
differing.ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааа ааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
Fig-7
а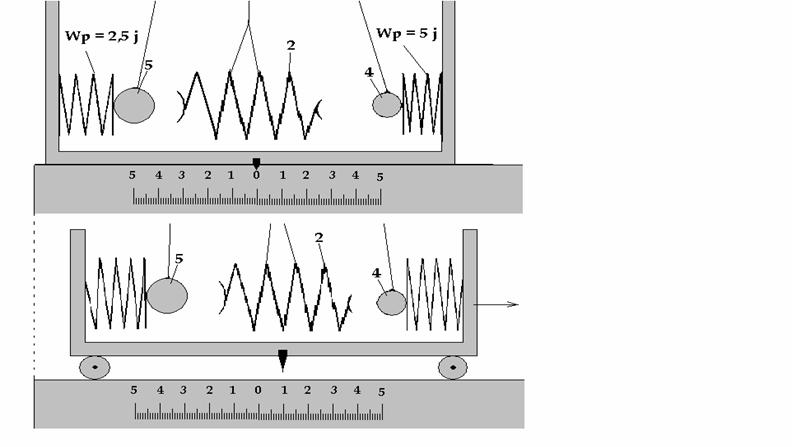
аааааааааааааааааа ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-8
The sense of this phenomena becomes clear
if compare the fig-7 with fig-8. In fig-7 we see: balls 4 and 5 at getting of equal
pulse have different kinetic energies and compress differently springs because that
pushcart stands still. If consider the fig-8, where pushcart can easy move,
during compression both of springs strive to level their resistances and forces to move the
pushcart.а The fig-8 demonstrates that
pushcart is displaced toward the stronger blow, got from lighter ball. Though
balls have an equal pulse, but because of that that they have different kinetic
energies and execute the different functioning, system centre changes its
position. The pushcart falls into closed system because that from outside does
not act any power.
The given experiment explains the
phenomenon about handgun; why at moment of the shooting bullet gains more
kinetic energy during inflaming the gunpowder in stem by comparison with
handgun. At automaton Kalashnikov bullet when leaving from stem has a kinetic
energy equal 2020j, but automaton it self has a kinetic energy equal to 5j. The
difference between two energies is 2015j.
See the fig-9.
Fig-9
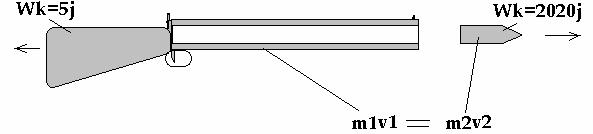
m1v1
(the pulse of bullet) = kinetic energy in 2020j
m2v2
(the pulse of the automaton) = kinetic energy in 5jаааа
аThe
bullet and handgun during shot get an equal pulse m1v1 = m2v2, hereinafter both
masses have a different kinetic energies and capable to execute different
functioning, and subsequently at collision with other object system centre is
changed. The bullet with its kinetic energy at collision with object will
reject it further, than handgun. The person, who shooted from a handgun, and
person, which is shooted, are standing in closed system therefore that from
outside does not influence any power. For count of the energy formed in the
handgun, one person has been knocked the more, and the second less. If follow
the Law of the conservation motion amount (the Law of the pulse) both must
knock equally and both of them should be displaced from the centre equally.
As a result of made experiments becomes
evident that action of the Law of the conservation of motion amount (the Law of
the pulse) exists until objects, got equal pulse, do not face with other objects.
The Law confirms that interaction of bodies, that are forming a closed system,
brings only to changing of motion amount between these bodies, but can not
change moving the system as integer: under any interaction between bodies,
forming closed system, velocity of the moving of the inertias centre does not
change. But experiment proves opposite: system centre is changed.аааааа
If take into account this theory then on
its base it is possible to construct the cosmic flying machine, which will be
able to move from one planet to another for count of the solar energy. For this
is necessary for correct calculations, in which is taken into account the
following: two different objects with equal pulses for count that that they
have different kinetic energies, will be able to execute the different
functioning for one and same time.аааааа
The physics is an experimental science.
This signifies
that physical laws become firmly established after undertaking frequentative
experience.
ааааа
What is
the sense of the discovered physical phenomenon?
аааааа
The Law of the conservation of energy for a long length of time is
declared absolute. Following the Law of the conservation of energy are made several
experiments which are offered to your attention. What is the sense of the discovered
physical phenomenon?
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа ааFig-1
а
 ааааа Imagine two cargoes made of steel in form
of a ball, greater ball has a mass of
ааааа Imagine two cargoes made of steel in form
of a ball, greater ball has a mass of
аааааааааа аааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа аFig-2
а
а Hereinafter
we shall examine fig-2: we release the ball 1 from height of
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааFig-3
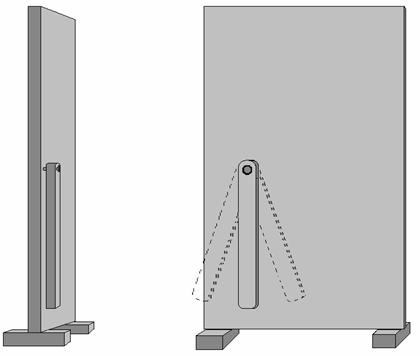
Further we make the experiment with
device, which consists of still body, and on it is installed a metallic peg,
which can move as pendulum. See the fig-3, where is represented specified
device.
аа
аа ааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
а
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа Fig-4
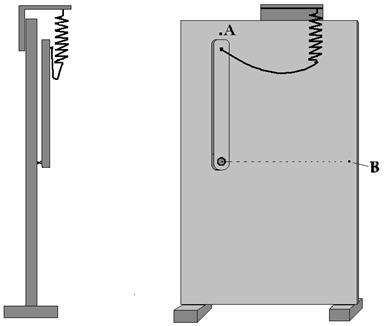
We lift the peg from lower point in higher
point (see the fig-4). In higher part of the body is bolted still a spring, the
lower part of which is united with a peg by means of cord.
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
а
а
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа Fig-5
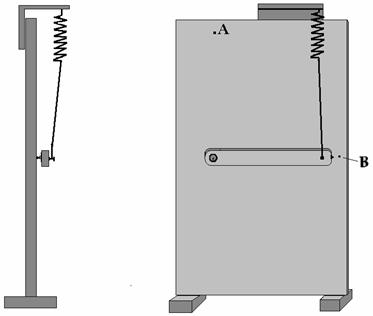
We have adjusted the length of the spring
so that peg at falling from point A has sprained it to the point B (see the fig-5).
The whole kinetic and potential energy of peg from point └ to point B was spent on spraining of
spring. We have measured only first, the most powerful blow peg, the further
fluctuations shall not take in reckoning.аа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааа ааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
а
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа ааFig-6
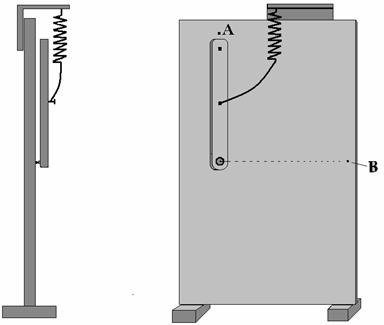
We make the second experiment: аlift the peg in point └ and shift the spring from edge to the
centre of the body. Carry the point of fastening of the spring with the peg
from edge to the centre of peg (see the fig-6).
а
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа Fig-7
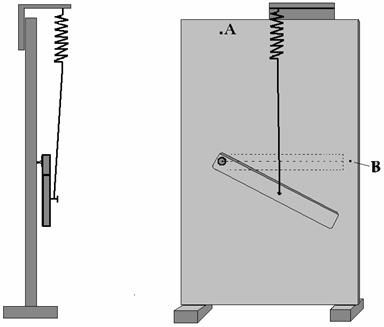
After we release
the peg that at falling it sprained the spring (see the fig-7).
аааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааа ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
а
At falling the peg will send to the spring
its whole kinetic and potential energy. In point B we take in reckoning only
the first blow and consider the energy of peg and spring. When making
frequentative experiments we came to a conclusion: when peg falls in point B
spring sprained equally, both in the first, and in second variant, but in second
variant peg does not lose whole kinetic energy and continues to sprain the
spring. If raise the peg from point ┬ to point └ in both cases are spent equal amounts
of energy. After frequentative measurements in point B we get 30 % difference
of energies. In all experiment participates same peg and same spring, and the
way from point └ to the point B forms 90º. If mgh
is unchangeable in all variants, then why in the first experiment in point B
get on 30 % energy less?
ааа
The Law of the conservation and conversions of energy: after any
process, occurring in closed system, its full energy does not change.
ааа
The mechanical energy is equal to an amount of kinetic and potential
energy:
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа
ааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааааа W = Wk
+ Wp
ааааа
The problem is concluded in that that not all results of experiment can
be explained on base of existing laws.
аааа The given material
is registered in institute of guard of the rights of knowledge-based property.
Address: Leonid Popusoi,
аааааааааааааа а
ааааааааааааааа Kishinev,
street Albisoara 80/4, ap.184.
ааааааааааааааа tel.
(373 22) 291675
ааааааааааааааа E-mail: popusoi@rambler.ru